您所在的位置:首页 - 科普 - 正文科普
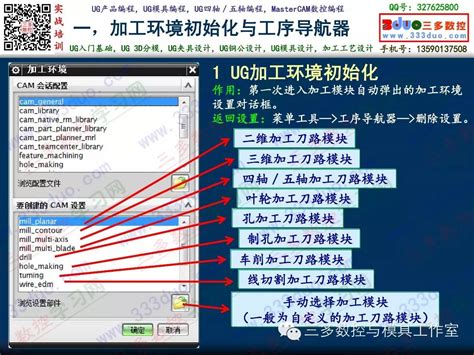
plc编程软件使用教程
![]() 芝祺
2024-05-12
【科普】
237人已围观
芝祺
2024-05-12
【科普】
237人已围观
摘要**Title:IntroductiontoPLCProgrammingSecurity**Intoday'sindustriallandscape,ProgrammableLogicControll
5.
Continuous Monitoring
: Implement continuous monitoring solutions to detect and respond to security incidents in realtime, minimizing the impact of potential breaches.6.
Regular Audits and Assessments
: Conduct regular security audits and penetration tests to evaluate the effectiveness of existing security controls and identify areas for improvement.PLCs execute tasks based on preprogrammed logic, making them vulnerable if their programming is compromised. Here are key aspects of PLC programming security:
2.
Authentication
: Implementing strong authentication mechanisms prevents unauthorized individuals from accessing the PLC programming interface. This includes using unique usernames, complex passwords, and multifactor authentication where possible.6.
Firmware Updates
: Keeping PLC firmware up to date is essential to patch known vulnerabilities and enhance security features. However, updates should be carefully tested in a controlled environment before deployment to avoid disrupting operations.2.
DefenseinDepth
: Adopt a layered approach to security by implementing multiple security controls at different levels, including network, host, and application layers.Despite the importance of securing PLC programming, several challenges exist:
3.
Data Encryption
: Encrypting PLC communication channels safeguards data integrity and confidentiality. Protocols like HTTPS and SSL/TLS can be employed to encrypt data transmitted between PLCs and programming devices.
5.
Auditing and Logging
: Logging all programming changes and access attempts provides a trail of events for auditing purposes. This helps in identifying suspicious activities and potential security breaches.3.
Vendor Collaboration
: Work closely with PLC vendors to stay updated on security patches, firmware updates, and best practices for securing their devices.Best Practices for PLC Programming Security
1.
Legacy Systems
: Many industrial facilities still rely on legacy PLCs with outdated security features or no security measures at all. Retrofitting these systems for enhanced security can be complex and costly.2.
Interoperability
: Integrating security measures across heterogeneous PLC systems from different vendors can be challenging due to compatibility issues and varying security standards.1.
Risk Assessment
: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and prioritize security measures based on potential impact and likelihood of exploitation.In today's industrial landscape, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are the backbone of automation systems, controlling everything from manufacturing processes to critical infrastructure. With their widespread use comes the imperative to ensure their programming remains secure from unauthorized access, tampering, or malicious attacks. Let's delve into the realm of PLC programming security to understand its importance, challenges, and best practices.
7.
Physical Security Measures
: Physical security measures such as enclosures, locks, and surveillance cameras protect PLCs from tampering or unauthorized access by intruders.4.
Human Factors
: Human error, negligence, or insider threats can compromise PLC programming security. Training personnel on security best practices and enforcing strict access controls are essential.PLC programming security is paramount in safeguarding industrial automation systems against cyber threats. By understanding the principles of access control, authentication, encryption, and integrity verification, organizations can implement effective security measures to protect their PLC programming from unauthorized access, tampering, and malicious attacks. By addressing challenges, adhering to best practices, and fostering collaboration between stakeholders, organizations can enhance the resilience of their industrial automation systems in the face of evolving cyber threats.
1.
Access Control
: Limiting physical and remote access to PLCs is crucial. Physical access should be restricted to authorized personnel only, while remote access should be encrypted and authenticated via secure channels.4.
Security Policies and Procedures
: Establish comprehensive security policies and procedures governing PLC programming, access control, incident response, and employee training.Challenges in PLC Programming Security
Title: Introduction to PLC Programming Security
4.
Integrity Verification
: Regularly verifying the integrity of PLC programming ensures that no unauthorized changes have been made. Hashing algorithms can be used to compare the current state of the program with a known, secure state.3.
Resource Constraints
: PLCs are often resourceconstrained devices with limited processing power and memory. Implementing robust security measures without impacting performance requires careful optimization.Understanding PLC Programming Security
To address these challenges and mitigate security risks, adhere to the following best practices:
By implementing robust security measures, staying vigilant against emerging threats, and fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can safeguard their PLC programming against potential cyber threats and ensure the uninterrupted operation of critical industrial processes.
Conclusion
Tags: 哈利波特4火焰杯 龙在江湖2 恶魔总裁的御用情人
版权声明: 免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户自行上传,若侵犯了您的权益,请联系我们处理,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052
最近发表
- 特朗普回应普京涉乌言论,强硬立场引发争议与担忧
- 民营企业如何向新而行——探索创新发展的路径与实践
- 联合国秘书长视角下的普京提议,深度解析与理解
- 广东茂名发生地震,一次轻微震动带来的启示与思考
- 刀郎演唱会外,上千歌迷的守候与共鸣
- 东北夫妻开店遭遇刁难?当地回应来了
- 特朗普惊人言论,为夺取格陵兰岛,美国不排除动用武力
- 超级食物在中国,掀起健康热潮
- 父爱无声胜有声,监控摄像头背后的温情呼唤
- 泥坑中的拥抱,一次意外的冒险之旅
- 成品油需求变天,市场趋势下的新机遇与挑战
- 警惕儿童健康隐患,10岁女孩因高烧去世背后的警示
- 提振消费,新举措助力消费复苏
- 蒙牛净利润暴跌98%的背后原因及未来展望
- 揭秘缅甸强震背后的真相,并非意外事件
- 揭秘失踪的清华毕业生罗生门背后的悲剧真相
- 冷空气终于要走了,春天的脚步近了
- 李乃文的神奇之笔,与和伟的奇妙转变
- 妹妹发现植物人哥哥离世后的崩溃大哭,生命的脆弱与情感的冲击
- 云南曲靖市会泽县发生4.4级地震,深入了解与应对之道
- 缅甸政府部门大楼倒塌事件,多名官员伤亡,揭示背后的故事
- 多方合力寻找失踪的十二岁少女,七天生死大搜寻
- S妈情绪崩溃,小S拒绝好友聚会背后的故事
- 缅甸遭遇地震,灾难之下的人间故事与影响深度解析
- 缅甸地震与瑞丽市中心高楼砖石坠落事件揭秘
- 揭秘ASP集中营,技术成长的摇篮与挑战
- 徐彬,整场高位压迫对海港形成巨大压力——战术分析与实践洞察
- ThreadX操作系统,轻量、高效与未来的嵌入式开发新选择
- 王钰栋脚踝被踩事件回应,伤势并不严重,一切都在恢复中
- 刘亦菲,粉色花瓣裙美神降临
- 三星W2018与G9298,高端翻盖手机的对比分析
- 多哈世乒赛器材,赛场内外的热议焦点
- K2两厢车,小巧灵活的城市出行神器,适合你的生活吗?
- 国家市监局将审查李嘉诚港口交易,聚焦市场关注焦点
- 提升知识水平的趣味之旅
- 清明五一档电影市场繁荣,多部影片争相上映,你期待哪一部?
- 美联储再次面临痛苦抉择,权衡通胀与经济恢复
- 家庭千万别买投影仪——真相大揭秘!
- 文物当上网红后,年轻人的创意与传承之道
- 手机解除Root的最简单方法,安全、快速、易操作
- 缅甸地震与汶川地震,能量的震撼与对比
- 2011款奥迪A8,豪华与科技的完美结合
- 广州惊艳亮相,可折叠电动垂直起降飞行器革新城市交通方式
- 比亚迪F3最低报价解析,性价比之选的购车指南
- 商业健康保险药品征求意见,行业内外视角与实用建议
- 官方动态解读,最低工资标准的合理调整
- 东风标致5008最新报价出炉,性价比杀手来了!
- 大陆配偶在台湾遭遇限期离台风波,各界发声背后的故事与影响
- 奔驰C级2022新款,豪华与科技的完美融合
- 大摩小摩去年四季度对A股的投资热潮