您所在的位置:首页 - 科普 - 正文科普
地球公转模型制作视频
![]() 艺涓
05-09
【科普】
593人已围观
艺涓
05-09
【科普】
593人已围观
摘要标题:探索地球公转:编程中的模拟与实践地球公转是天文学中基础而重要的概念,也是人类社会发展的重要背景之一。在编程中,模拟地球公转可以是一个有趣且富有挑战性的项目,涉及到数学、物理和计算机科学等多个领域
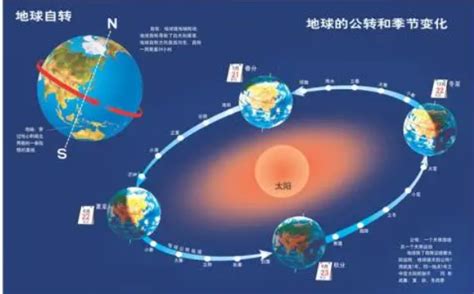
探索地球公转:编程中的模拟与实践
地球公转是天文学中基础而重要的概念,也是人类社会发展的重要背景之一。在编程中,模拟地球公转可以是一个有趣且富有挑战性的项目,涉及到数学、物理和计算机科学等多个领域的知识。本文将介绍如何利用编程语言来模拟地球公转,并提供一些指导建议和实践方法。
1. 确定模拟的范围和目标
在开始编程之前,首先需要确定模拟的范围和目标。地球公转是太阳系中的一部分,因此可以选择模拟整个太阳系的运动,或者仅关注地球与太阳之间的关系。你也可以选择是否包括其他天体,如月球、其他行星等。
2. 选择编程语言和工具
在确定模拟的范围后,需要选择合适的编程语言和工具来实现。常用的选择包括:
Python:Python是一种简单易学且功能强大的编程语言,拥有丰富的科学计算库(如NumPy、matplotlib),适合进行科学计算和模拟。
JavaScript:如果你想将模拟展示在网页上,JavaScript是一个很好的选择,可以利用HTML和CSS来创建交互式的模拟。
MATLAB:MATLAB是一种专业的科学计算软件,提供了丰富的工具箱,适用于复杂的数学和物理模拟。
选择合适的工具取决于你的偏好、项目需求和已有的技能水平。
3. 实现地球公转模拟
使用Python实现地球公转模拟的示例代码:
```python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Constants
G = 6.67430e11 gravitational constant (m^3 kg^1 s^2)
M = 1.989e30 mass of the sun (kg)
m = 5.972e24 mass of the earth (kg)
r = 149.6e9 mean distance from the earth to the sun (m)
v = 29780 mean orbital speed of the earth (m/s)
Initial conditions
x0 = r
y0 = 0
vx0 = 0
vy0 = v
Time parameters
t_start = 0
t_end = 365 * 24 * 60 * 60 1 year (s)
dt = 3600 time step (s)
Arrays to store data
t_values = np.arange(t_start, t_end, dt)
x_values = np.zeros_like(t_values)
y_values = np.zeros_like(t_values)
Euler's method for numerical integration
x = x0
y = y0
vx = vx0
vy = vy0
for i, t in enumerate(t_values):
r = np.sqrt(x
2 y
2)ax = G * M * x / r**3
ay = G * M * y / r**3
x = vx * dt
y = vy * dt
vx = ax * dt
vy = ay * dt
x_values[i] = x
y_values[i] = y
Plot the orbit
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(x_values, y_values)
plt.title('Earth Orbit Simulation')
plt.xlabel('x (m)')
plt.ylabel('y (m)')
plt.gca().set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
```
使用JavaScript和HTML实现交互式地球公转模拟的示例代码:
```html