您所在的位置:首页 - 百科 - 正文百科
刀具路径仿真不包括
![]() 智媚
2024-04-23
【百科】
234人已围观
智媚
2024-04-23
【百科】
234人已围观
摘要**Title:IntroductiontoToolPathProgramminginCNCMachining**InComputerNumericalControl(CNC)machining,to
Title: Introduction to Tool Path Programming in CNC Machining
In Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining, tool path programming is a crucial aspect that determines the movement of the cutting tool to create the desired part. Let's delve into the fundamentals and key considerations of tool path programming.
Understanding Tool Path Programming:
Tool path programming involves generating a sequence of instructions that guide the CNC machine's movements to shape the workpiece accurately. These instructions dictate the tool's trajectory, speed, feed rate, and orientation during the machining process.
Key Components of Tool Path Programming:
1.
CAD Model Interpretation:
Tool path programming begins with interpreting the ComputerAided Design (CAD) model of the part to be machined. This involves analyzing the geometry, dimensions, and features of the part.2.
CAM Software:
ComputerAided Manufacturing (CAM) software is used to generate tool paths based on the CAD model and machining requirements. CAM software allows programmers to define parameters such as cutting depths, tool selection, and cutting strategies.3.
Tool Selection:
Choosing the appropriate cutting tools is essential for efficient machining. Factors such as material type, part geometry, surface finish requirements, and cutting forces influence tool selection.4.
Cutting Strategies:
Tool path strategies vary depending on the part geometry and machining objectives. Common strategies include contouring, pocketing, profiling, drilling, and adaptive machining. Each strategy aims to optimize tool movement for maximum efficiency and surface quality.5.
Feed Rate Optimization:
Determining the optimal feed rate ensures efficient material removal while maintaining machining accuracy and surface finish. Feed rates are adjusted based on factors like tool material, cutting conditions, and part geometry.6.
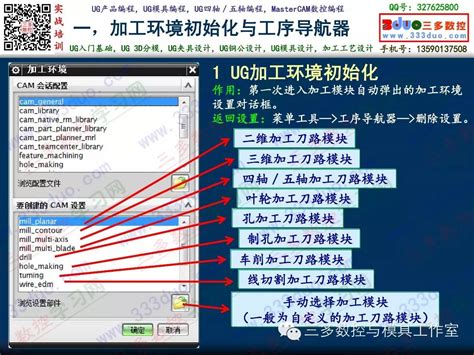
Toolpath Simulation:
Before executing the program on the CNC machine, tool paths are simulated to verify machining operations, detect potential collisions, and optimize cutting parameters. Simulation helps prevent costly errors and ensures safe machining.Best Practices for Tool Path Programming:
1.
Start with a Solid CAD Model:
A welldefined CAD model serves as the foundation for accurate tool path generation. Ensure the model is free from errors and includes all necessary features.2.
Consider Machining Constraints:
Account for machine capabilities, tooling limitations, and material properties when designing tool paths. Avoid sharp changes in direction, excessive tool engagement, and other factors that could compromise machining quality or tool life.3.
Optimize Cutting Parameters:
Finetune cutting parameters such as spindle speed, feed rate, and depth of cut to balance productivity and tool life. Experiment with different parameters to find the optimal balance for each machining operation.4.
Use Simulations Wisely:
Regularly simulate tool paths to validate programming decisions and identify potential issues before machining begins. Invest in advanced simulation software that accurately models machine behavior and material removal processes.5.
Continuous Improvement:
Keep abreast of advancements in CAM software, cutting tools, and machining techniques to continually improve tool path programming efficiency and quality.Conclusion:
Tool path programming is a critical aspect of CNC machining, influencing productivity, accuracy, and part quality. By understanding the fundamentals of tool path programming and adhering to best practices, manufacturers can optimize machining processes and achieve superior results.
Tags: 毁灭战士电影 经典纸牌接龙 雪佛兰科迈罗zl1 三国群英传7中文版 百度搜索风云榜
版权声明: 免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户自行上传,若侵犯了您的权益,请联系我们处理,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052
上一篇: 计算机中占比计算公式
下一篇: mc粗铁怎么获得
最近发表
- 特朗普回应普京涉乌言论,强硬立场引发争议与担忧
- 民营企业如何向新而行——探索创新发展的路径与实践
- 联合国秘书长视角下的普京提议,深度解析与理解
- 广东茂名发生地震,一次轻微震动带来的启示与思考
- 刀郎演唱会外,上千歌迷的守候与共鸣
- 东北夫妻开店遭遇刁难?当地回应来了
- 特朗普惊人言论,为夺取格陵兰岛,美国不排除动用武力
- 超级食物在中国,掀起健康热潮
- 父爱无声胜有声,监控摄像头背后的温情呼唤
- 泥坑中的拥抱,一次意外的冒险之旅
- 成品油需求变天,市场趋势下的新机遇与挑战
- 警惕儿童健康隐患,10岁女孩因高烧去世背后的警示
- 提振消费,新举措助力消费复苏
- 蒙牛净利润暴跌98%的背后原因及未来展望
- 揭秘缅甸强震背后的真相,并非意外事件
- 揭秘失踪的清华毕业生罗生门背后的悲剧真相
- 冷空气终于要走了,春天的脚步近了
- 李乃文的神奇之笔,与和伟的奇妙转变
- 妹妹发现植物人哥哥离世后的崩溃大哭,生命的脆弱与情感的冲击
- 云南曲靖市会泽县发生4.4级地震,深入了解与应对之道
- 缅甸政府部门大楼倒塌事件,多名官员伤亡,揭示背后的故事
- 多方合力寻找失踪的十二岁少女,七天生死大搜寻
- S妈情绪崩溃,小S拒绝好友聚会背后的故事
- 缅甸遭遇地震,灾难之下的人间故事与影响深度解析
- 缅甸地震与瑞丽市中心高楼砖石坠落事件揭秘
- 揭秘ASP集中营,技术成长的摇篮与挑战
- 徐彬,整场高位压迫对海港形成巨大压力——战术分析与实践洞察
- ThreadX操作系统,轻量、高效与未来的嵌入式开发新选择
- 王钰栋脚踝被踩事件回应,伤势并不严重,一切都在恢复中
- 刘亦菲,粉色花瓣裙美神降临
- 三星W2018与G9298,高端翻盖手机的对比分析
- 多哈世乒赛器材,赛场内外的热议焦点
- K2两厢车,小巧灵活的城市出行神器,适合你的生活吗?
- 国家市监局将审查李嘉诚港口交易,聚焦市场关注焦点
- 提升知识水平的趣味之旅
- 清明五一档电影市场繁荣,多部影片争相上映,你期待哪一部?
- 美联储再次面临痛苦抉择,权衡通胀与经济恢复
- 家庭千万别买投影仪——真相大揭秘!
- 文物当上网红后,年轻人的创意与传承之道
- 手机解除Root的最简单方法,安全、快速、易操作
- 缅甸地震与汶川地震,能量的震撼与对比
- 2011款奥迪A8,豪华与科技的完美结合
- 广州惊艳亮相,可折叠电动垂直起降飞行器革新城市交通方式
- 比亚迪F3最低报价解析,性价比之选的购车指南
- 商业健康保险药品征求意见,行业内外视角与实用建议
- 官方动态解读,最低工资标准的合理调整
- 东风标致5008最新报价出炉,性价比杀手来了!
- 大陆配偶在台湾遭遇限期离台风波,各界发声背后的故事与影响
- 奔驰C级2022新款,豪华与科技的完美融合
- 大摩小摩去年四季度对A股的投资热潮